
Use your knowledge and skills to help others succeed.ĭon't be wasteful protect our environment. Displacement Equations for Falling Objects.
Freefall position kinematic equation for free#
Displacement-Velocity Gravity Equations Kinematic Equation for Free Fall Acceleration ay -g 9.80 m/s2 (a of y b/c vertical direction) Free Fall of an object DROPPED Vo is ZERO Up is Positive ay -g -9.80 m/s2 use y instead of x b/c vertical position Free Fall of an object THROWN DOWNWARD Vo is negative (b/c up is positive) Vo is NOT zero ay -g 9.I will try to get back to you as soon as possible.Ĭlick on a button to bookmark or share this page through Twitter, Facebook, email, or other services: Top-rated books on Advanced Gravity Physicsĭo you have any questions, comments, or opinions on this subject? If so, send an email with your feedback. Top-rated books on Simple Gravity Science (Notice: The School for Champions may earn commissions from book purchases) Kinematic Equations and Free Fall - Physics Classroom Books Gravity Calculations - Earth - Calculator The following equations allow you to calculate the displacement the object falls until it reaches a given velocity or after a given period of time: Solutionĭisplacement is the change in position from the starting point in a specific direction. Those equations are useful, but they dont give exact values for velocity or acceleration, just an average. Note (1): Because the air resistance is neglected, the time the ball is going up is half the time it is going down. To solve this free fall problem, it is necessary to know some notes about the free-falling objects. Weve already learned about the equations for average velocity and average acceleration. Over 15 practice problems on kinematics equations are solved which are helpful for high school physics. If t = 4 seconds and g = 9.8 m/s 2, find the displacement the object has fallen. Kinematics is a branch of physics that models the motion of objects using position, velocity, acceleration, and time. If v = 75 ft/s, how far has the object fallen? Solution The following examples illustrate applications of the equations. Since v i = 0 for a dropped object, the equation reduces to: ( See Derivation of Displacement-Time Gravity Equations for details of the derivations.) The general gravity equation for the displacement with respect to time is: Since the object is moving downward from the starting point, both y and v are positive numbers.ĭisplacement of a falling object as a function of velocity or time Displacement with respect to time g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s 2 or 32 ft/s 2).v is the vertical velocity in m/s or ft/s.Answer: (a) a (v u)/t 35 (-20)/0.02 2750 m/s 2 (b) v2 u2 + 2as s ( v2 u2 ) / (2a) (35×35 20×20) / (2×2750) 0. Freefall as the term says, is a body falling freely because of the gravitational pull of our earth. y is the vertical displacement in meters (m) or feet (ft) (a) the acceleration of the ball during the hit (b) the distance moved by the ball during the hit.Since the initial velocity v i = 0 for a dropped object, the equation reduces to: ( See Derivation of Displacement-Velocity Gravity Equations for details of the derivation.) When skydiving, jumpers jump out of airplanes \( 14,000\,\mathrm, \) all while experiencing an effect, known to avid jumpers, as "relative wind." Relative wind allows jumpers to deflect the rushing air over their bodies and provides them with very accurate control of what they do in the air from flips, spins, etc.The general gravity equation for displacement with respect to velocity is:
Freefall position kinematic equation how to#

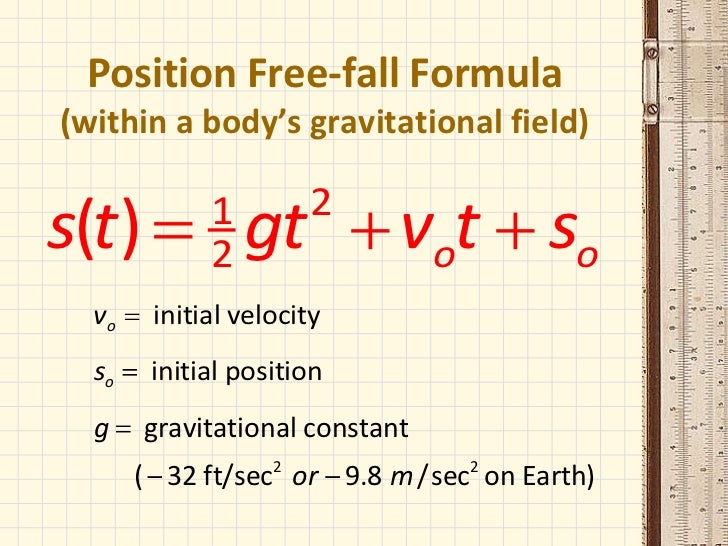
acceleration, velocity, position, constant, changing, and zero, why the solution below is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
